Peripheral Vascular Treatment Market Thrives Due To Tech Innovation, Socioeconomic Conditions
By Dr. Kamran Zamanian and Rami Faour, iData Research Inc.
The need to treat peripheral arterial disease (PAD) has given rise to a multi-billion dollar market for peripheral vascular (PV) medical devices. Three main factors are driving robust growth in the US: the demographic shift, technological innovation, and increases in healthcare expenditures. In comparison to other markets for cardiovascular devices, this market has witnessed outsized growth in recent years in part due to increasing public awareness and improvements in stent technology, which have expanded the potential patient pool. In addition to the aging U.S. population and increasing reimbursement rates for procedures like atherectomy, these factors will collectively contribute to overall growth in 2014.
However, the market is undergoing dramatic developments that question the sustainability of growth and profitability. In fact, several important markets, including bare-metal stents and percutaneous balloon angioplasty (PTA) balloons, are beginning to show signs of saturation. In seeking above-average growth, leading companies are actively pouring millions of dollars towards the development and acquisition of new drug-eluting technology. While skepticism on the efficacy of these devices is pervasive among a substantial portion of market participants and end users, several companies stand the chance of pioneering technology that will alter the lives of patients and, in the process, transform the peripheral vascular device market.
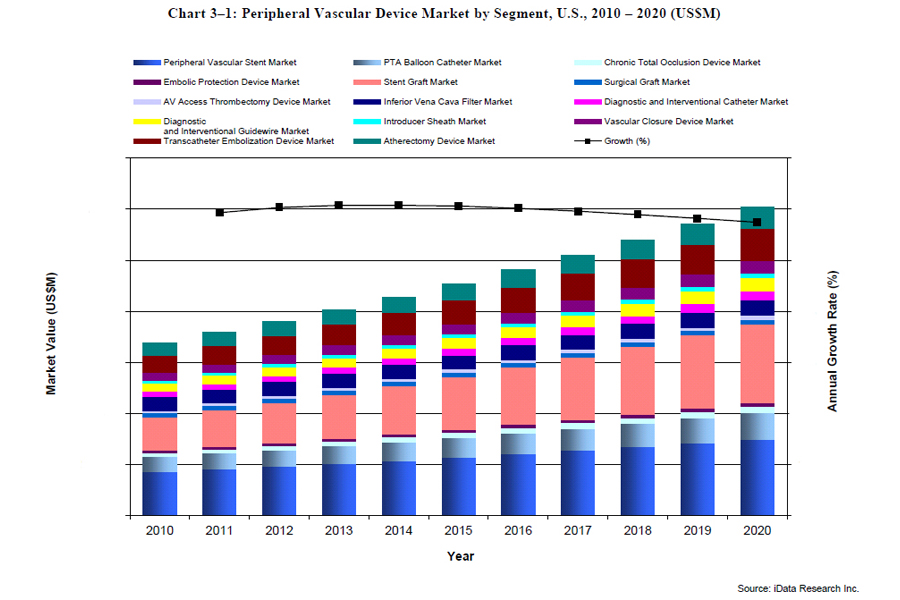
In the United States, PAD affects nearly 10 million people. PAD is manifested through the accumulation of plaque on the arterial walls, which impedes blood flow to vital tissue and organs. The main method of treatment has been the use of balloon angioplasty and stenting. Combined, these two markets will generate nearly $1.3 billion in 2013, or nearly 30 percent of the entire PV medical device markets. The increasing risk for stroke and heart attack associated with PAD are well documented, and medical institutions are aware of the benefits associated with endovascular treatment of PAD. People older than 65 are particularly at risk for PAD, and the aging U.S. population will continue to drive demand for treatment procedures. In the U.S., people over 65 currently represent 13 percent of the population. This figure is expected to grow to reach 19 percent by 2030, representing annual growth of 2 percent. This demographic shift will continue to buoy demand for stents and PTA balloons in the near future.
However, in assessing future growth in these markets, signs point toward market saturation. Bare-metal stents, with few exceptions, are increasingly perceived as commodities by end users, and the main selling point has become price. Stents for the treatment of iliac and femoropoliteal restenosis together comprise nearly all bare-metal stent applications. The prices of stents in these segments continue to decline on an annual basis as companies engage in price wars. The fact that the market is extremely fragmented will only reinforce this trend.
In addition to price erosion, the penetration rate in the peripheral stent market has increased substantially over the past decade, and while the potential market for peripheral vascular devices is ostensibly 10 million patients, the practical number of patients that can be treated is only 20 to 35 percent of this figure. This is due to several factors that prevent the remainder of the population from having access or the resources in order to receive the appropriate treatment. This assumption is supported by trends seen in other medical device markets, including implantable defibrillators and coronary stents, where the double digit growth has been replaced by 4 to 5 percent as penetration rates plateaued. The market for peripheral stents has been undergoing a similar trend, and growth in this market is expected to decline as the market matures.
As the profit margins in both the stent and PTA balloon market continue to erode, companies are shifting their focus from the sale of bare-metal stents towards investing in new technology that will generate above-average growth. Technological innovation has played a key role in propelling growth in several areas of the PV market. Over the past decade, longer self-expanding nitinol stents proved superior to balloon expandable stents in the treatment of occluded arteries. With the majority of companies boasting a portfolio of effective bare-metal stents, companies are increasingly shifting their focus onto the new frontier of drug-eluting technology in an effort to garner above average growth.
This is being done through the development of drug-eluting stents (DES) and drug-coated balloons (DCB). DES were first approved for coronary applications in 2003. A decade later, the first DES received FDA approval for the treatment of femoropopliteal arteries. DES was a truly disruptive technology in the coronary stent market, replacing over 80 percent of the bare-metal stents. In peripheral applications, the efficacy of DES has been questioned. Initial attempts to implement this technology were unsuccessful. Clinical results showed no significant advantage to using DES over bare-metal stents, and efforts to launch the first DES were ultimately abandoned.
Signs of optimism emerged in 2013, when Cook Medical published four-year results showing superior patency rates for their Zilver PTX DES in comparison to bare-metal stents for superficial femoral artery (SFA) treatment. Moreover, the product was granted additional reimbursement in late 2013. Although this device has been on the market in Europe since 2009, its widespread adoption has been hampered by the lack of reimbursement in certain countries and reluctance by physicians to use stents. The device is expected to have greater success in the U.S. market, and if Cook captures as little as 5 percent of the SFA stenting procedures, this will translate into revenue of $20 million to $30 million. Widespread adoption of this product for SFA treatment will be hindered by its higher price in comparison to bare-metal stents. Nonetheless, if clinical results continue to confirm the superiority of DES, it is expected that drug-eluting stents will play a role in the peripheral vascular market, albeit not to the same extent that they have in the coronary field.
In contrast to DES, the investment in DCB is more substantial, with several companies, including Medtronic and C. R. Bard, vying to launch the first device in the U.S. Drug-coated balloons have been launched in Europe and have generated substantial revenue for market leader Medtronic. Drug-coated balloons will not only affect the standard PTA balloon market, but will also threaten the stent market. While most agree that stents will remain necessary for the treatment of heavily calcified lesions and cases of elastic recoil, DCBs have the potential to be the golden standard of treatment by providing an effective and cost-saving solution.
The third factor that has led to substantial growth in the peripheral vascular market, most prominently in the atherectomy device and inferior vena cava filter (IVCF) markets, is the favorable reimbursement structure in the U.S. Reimbursement rates for atherectomy have been increasing at nearly 5 percent per annum. The attractive reimbursement structure has led to a dynamic market with new technological advancements and expected new entrants in 2014. Companies such as Cardiovascular Systems Inc. continue to post earnings growth in excess of 20 percent as of Q3 2013.
However, the long-term clinical efficacy of these devices has not been established, and concerns over appropriate usage may surface. In fact, the disparity in the usage of atherectomy and IVCF is stark when comparing the U.S. to the European Union. The usage of IVCF in Sweden serves as an example. The U.S. population is nearly 30 times as large as the population of Sweden; however, for every IVCF used in Sweden, approximately 8,000 filters are used in the U.S. Moreover, the U.S. market for atherectomy devices constitutes over 95 percent of the global atherectomy market due to favorable reimbursement, which is absent in the EU. It is expected that over the long term, increasing appropriate usage scrutiny will temper growth in these markets and may cause the backlash recently seen in the coronary stent market, in which over-stenting is now thought to occur in over a third of all cases.
In conclusion, the market for peripheral vascular medical devices is highly dynamic. The saturation seen in the prominent stent and PTA balloon markets has driven companies to innovate and provide more effective treatment options. In a changing healthcare landscape characterized by increasing budgetary constraints and an emphasis on provider accountability, the companies that pioneer and effectively market drug-eluting technology for peripheral treatment stand to dominate the competitive landscape and transform the treatment of vascular disease.
The information in this article was taken from a global report series entitled Peripheral Vascular Devices Market, covering the following market segments: peripheral vascular stents, PTA balloon catheters, atherectomy devices, chronic total occlusion (CTO) devices, embolic protection devices, stent grafts, surgical grafts, AV access thrombectomy devices, inferior vena cava filters, diagnostic and interventional catheters, diagnostic and interventional guidewires, introducer sheaths, vascular closure devices, and transcatheter embolization devices.
About iData Research
iData Research is an international market research and consulting group focused on providing market intelligence for medical device and pharmaceutical companies. iData covers research in: infusion therapy, peripheral vascular, vascular-access, drug-delivery, and more.
